Are you preparing for your CBSE Class 10 Science exam and want to score full marks in the Case Study Questions section? In this post, we bring you Case Study based questions for Chapter 1: Chemical Reactions and Equations along with detailed solutions in an interactive quiz format.

These questions are designed according to the latest CBSE exam pattern and will help you master important concepts like types of chemical reactions, balancing equations, and real-life applications of reactions.
Why Practice Case Study Questions?
CBSE has introduced case-based questions to test your understanding and application skills. These questions are often scenario-based and require you to analyze data, interpret reactions, and apply concepts.
Case study-based questions are now a major part of CBSE Class 10 Science exams, testing not only your memory but also your understanding and application skills.
In Chapter 1 – Chemical Reactions and Equations, these questions focus on identifying reaction types, balancing equations, and predicting products.
If you want full marks in the board exam, practicing these case study-based questions with detailed answers is essential.
Interactive Quiz – Case Study Based Questions
(Attempt the questions below and check your answers instantly)
📚 Case Study 1: Burning of Magnesium Ribbon
Clean a magnesium ribbon about 2 cm long by rubbing it with sandpaper. Hold it with a pair of tongs. Burn it using a spirit lamp or burner and collect the ash so formed in a watch-glass.
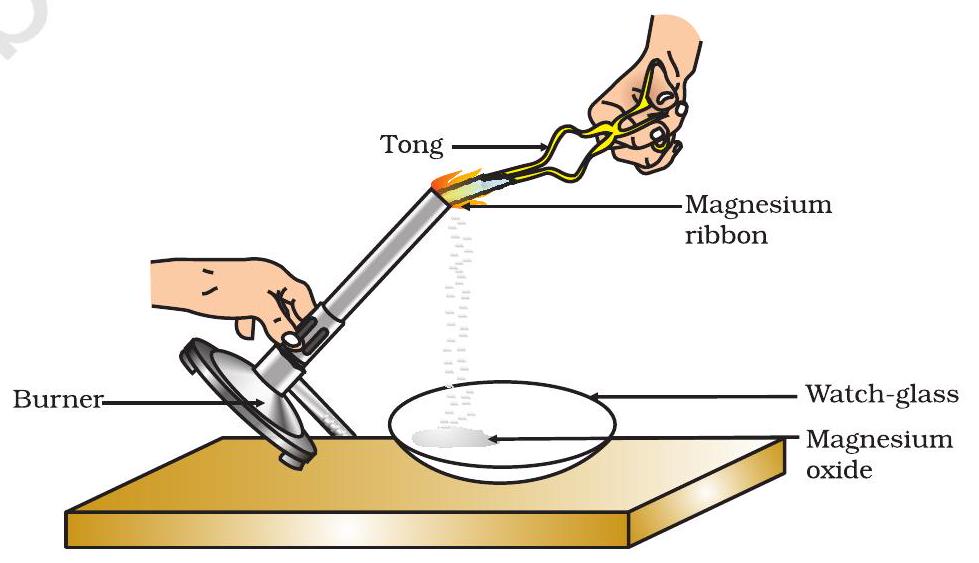
Based on the above experiment, answer the following questions:
Q1. Magnesium ribbon is rubbed before burning because it has a coating of
Magnesium ribbon develops a layer of basic magnesium oxide when exposed to air, which needs to be removed for proper combustion.
Q2. What is the colour of magnesium ribbon?
Magnesium ribbon has a silvery-grey metallic appearance.
Q3. What is the chemical name of the powder obtained in the activity?
When magnesium burns in air, it combines with oxygen to form magnesium oxide (MgO), which appears as white ash.
Q4. Which compound is formed when the powder obtained reacts with water?
Magnesium oxide (MgO) reacts with water to form magnesium hydroxide [Mg(OH)₂]: MgO + H₂O → Mg(OH)₂
📚 Case Study 2: Electrolysis of Water
Take a plastic mug, drill two holes at its base and insert carbon electrodes. Connect these electrodes to a 6 volt battery. Fill the mug with water such that the electrodes are immersed. Add a few drops of dilute sulphuric acid to the water. Take two test tubes filled with water and invert them over the two carbon electrodes. Switch on the current and leave the apparatus undisturbed for some time.
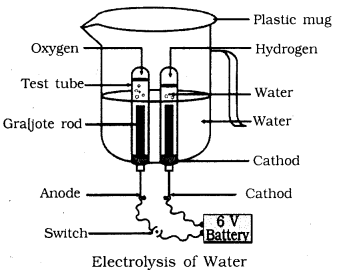
Answer the following questions:
Q5. What is the ratio in which hydrogen and oxygen are present in water by volume?
Hydrogen and oxygen are present in water in the ratio 2:1 by volume. Water molecule (H₂O) contains 2 hydrogen atoms and 1 oxygen atom.
Q6. Which electrodes are used in this activity?
Graphite (carbon) electrodes are used in electrolysis of water as they are inert and good conductors of electricity.
Q7. Where is hydrogen gas collected?
Hydrogen gas is collected at the cathode (negative electrode) during electrolysis of water.
Q8. Which of the following is an endothermic process?
Electrolysis is an endothermic process as it requires continuous supply of electrical energy to proceed.
📚 Case Study 3: Thermal Decomposition of Ferrous Sulphate
Take about 2 g ferrous sulphate crystals in a dry boiling tube. Heat the boiling tube over the flame of a burner or spirit lamp. In this reaction you can observe that a single reactant breaks down to give simpler products. This is a decomposition reaction. Ferrous sulphate crystals (FeSO₄·7H₂O) lose water when heated and the colour of the crystals changes. It then decomposes to ferric oxide (Fe₂O₃), sulphur dioxide (SO₂) and sulphur trioxide (SO₃). Ferric oxide is a solid, while SO₂ and SO₃ are gases.
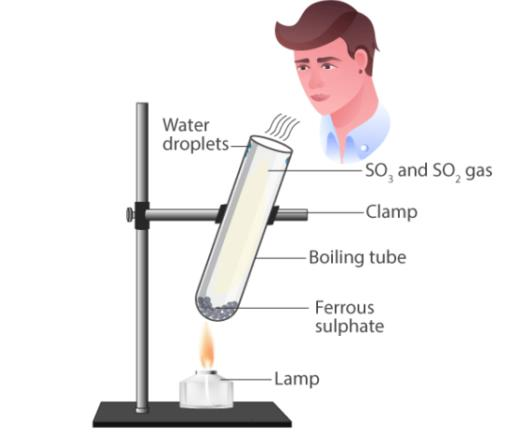
Answer the following questions:
Q9. What can we observe in this activity?
During decomposition of ferrous sulphate, we observe water vapor evolution, color change from green to brown, and smell of burning sulphur due to SO₂ gas.
Q10. What is the colour of iron oxide?
Ferric oxide (Fe₂O₃) formed during decomposition is reddish-brown in color.
Q11. What compound is formed when sulphur dioxide is passed through water?
When SO₂ dissolves in water, it forms sulphurous acid (H₂SO₃): SO₂ + H₂O → H₂SO₃
📚 Case Study 4: Double Displacement Reaction
The double displacement reaction is a type of chemical reaction where two compounds react and the cation and anion of the two reactants switch places forming 2 new products. The ionic compounds considered as reactants are water soluble. One of the products is formed as a precipitate or as a gas which is water soluble.
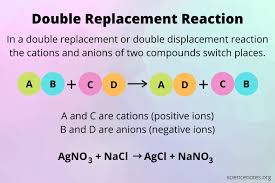
Answer the following questions:
Q12. The reaction between lead nitrate and potassium iodide is an example of:
Lead nitrate and potassium iodide undergo double displacement reaction: Pb(NO₃)₂ + 2KI → PbI₂ + 2KNO₃
Q13. What was the color of the precipitate formed when Lead nitrate reacts with Potassium iodide?
Lead iodide (PbI₂) formed as precipitate is bright yellow in color.
Q14. Which metallic spoon can be used to stir Lead nitrate solution?
Silver is less reactive than lead and won’t react with lead nitrate solution, making it safe to use.
📚 Case Study 5: Corrosion of Metals
We have observed that iron articles are shiny when new, but get coated with a reddish brown powder when left for some time. This process is commonly known as rusting of iron. Some other metals also get tarnished in this manner. When a metal is attacked by substances around it such as moisture, acids, etc., it is said to corrode and this process is called corrosion.

Answer the following questions:
Q15. The chemical formula of rust is:
Rust is hydrated iron(III) oxide with formula Fe₂O₃·xH₂O where x represents variable amount of water.
Q16. Which of the following metal is highly corrosive?
Among the given options, Zinc is most prone to corrosion as it is more reactive. Gold and silver are noble metals and resist corrosion.
Q17. If a metal undergoes uniform corrosion it becomes:
Uniform corrosion causes gradual thinning of metal as material is lost uniformly from the surface.
📚 Case Study 6: Displacement Reactions
Rishabh wanted to study displacement reactions. He knows that he needs a metal and a salt solution of a different metal. So, he takes two tubes T₁ and T₂, out of which in T₁, he placed a copper wire in iron sulphate solution and in T₂, he placed an iron nail in copper sulphate solution.
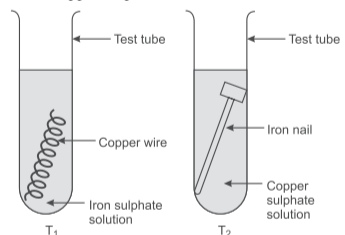
Answer the following questions:
Q18. Based on the above passage which test tube will undergo displacement reaction?
Only T₂ will undergo displacement reaction as iron is more reactive than copper and can displace it from copper sulphate solution.
Q19. Identify the balanced chemical equation for reaction taking place in T₂:
The balanced equation is: Fe(s) + CuSO₄(aq) → FeSO₄(aq) + Cu(s)
Q20. State the change(s) that is/are observed in T₂:
Both color change from blue to green and brown copper coating on iron nail are observed.
Q21. What will happen if zinc wire is used in place of copper wire in T₁?
Zinc is more reactive than iron, so it will displace iron from iron sulphate solution: Zn + FeSO₄ → ZnSO₄ + Fe
Q22. What will happen if silver nitrate is used in place of iron sulphate in T₁?
Copper can displace silver from silver nitrate: Cu + 2AgNO₃ → Cu(NO₃)₂ + 2Ag
📚 Case Study 7: Marble and Calcium Carbonate
Marble’s popularity began in ancient Rome and Greece, where white and off-white marble were used to construct a variety of structures, from hand-held sculptures to massive pillars and buildings. Marble contains calcium carbonate which reacts with acids.

Answer the following questions:
Q23. The substance not likely to contain CaCO₃ is:
Calcined gypsum is calcium sulphate (CaSO₄), not calcium carbonate. Dolomite, marble, and sea shells all contain CaCO₃.
Q24. Marble statues are corroded when they come into contact with polluted rain water. The main reason is:
Acid rain (polluted water) is acidic due to dissolved SO₂ and NO₂, which reacts with CaCO₃ in marble causing corrosion.
Q25. Gas obtained when CaCO₃ decomposes is used in which biochemical process?
CO₂ gas obtained from decomposition of CaCO₃ is used in photosynthesis by plants.
Q26. Calcium oxide can be reduced to calcium by heating with sodium metal. Which compound acts as oxidising agent?
Calcium oxide (CaO) acts as oxidising agent as it gets reduced to calcium while sodium gets oxidized.
📚 Case Study 8: Reaction between MnO₂ and HCl
The reaction between MnO₂ with HCl produces a gas with bleaching abilities. This is an important redox reaction used in laboratory preparation of chlorine gas.
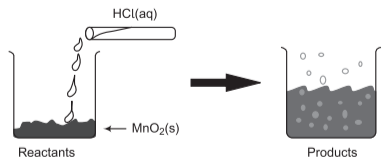
Answer the following questions:
Q27. The chemical reaction between MnO₂ and HCl is an example of:
This is a redox reaction where MnO₂ is reduced and HCl is oxidized to produce Cl₂ gas.
Q28. In the MnO₂ + HCl reaction, identify the correct statement:
MnO₂ is reduced (Mn⁴⁺ to Mn²⁺) while HCl is oxidized (Cl⁻ to Cl₂).
Q29. In the MnO₂ + HCl reaction, name the reducing agent:
HCl acts as reducing agent as it reduces MnO₂ while itself getting oxidized to Cl₂.
Q30. What will happen if we take dry HCl gas instead of aqueous solution of HCl?
Dry HCl gas will not react as ions are needed for the reaction, which are present only in aqueous solution.
Q31. Which of the following methods is NOT used for prevention of corrosion?
Heating does not prevent corrosion. Greasing, painting, and plating are methods to prevent corrosion by preventing contact with air and moisture.
Q32. Copper gets corroded in presence of:
Copper reacts with H₂S gas in presence of moisture to form black copper sulphide (CuS) coating.
📚 Case Study 9: Observations in Chemical Reactions
When chemical reactions occur, various observable changes take place. These changes help us identify that a chemical reaction has occurred. Common observations include formation of precipitate, evolution of gas, change in color, change in temperature, and change in state.
Answer the following questions:
Q33. When carbon dioxide is passed through lime water:
When CO₂ is passed through lime water [Ca(OH)₂], it forms calcium carbonate (CaCO₃) which is insoluble and makes the solution milky.
Q34. Whenever a chemical reaction occurs, we get to see:
All these are possible observations in chemical reactions – precipitate formation, gas evolution, and color change.
Q35. Consider reaction: S(s) + O₂(g) → SO₂. State of SO₂ in this reaction is:
Sulphur dioxide (SO₂) is a gas at room temperature and is produced in gaseous state in this reaction.
Q36. Which one of the given processes involves chemical reactions:
Heating copper wire causes oxidation of copper to form copper oxide (CuO), which is a chemical reaction. Others are physical changes.
📚 Case Study 10: Decomposition Reactions
Decomposition reaction refers to breakdown of a compound by passing current, heat or exposing it to light. In general, the decomposition reaction can be represented by AB → A + B. The decomposition reaction requires energy in the form of heat, electricity or light to break the bonds.
Answer the following questions:
Q37. CO₂ obtained by the complete decomposition of 20 g CaCO₃ at STP is:
20g CaCO₃ = 0.2 mol. CaCO₃ → CaO + CO₂. 0.2 mol CO₂ at STP = 0.2 × 22.4 = 4.48 L
Q38. Decomposition of hydrogen peroxide to give H₂O + O₂ is an example of:
2H₂O₂ → 2H₂O + O₂ is a disproportionation reaction where oxygen is both oxidized and reduced.
Q39. The reaction 2Pb(NO₃)₂ → 2PbO + 4NO₂ + O₂ is a type of:
This is a thermal decomposition reaction where lead nitrate breaks down into simpler products on heating.
Q40. On passing current to acidified water we get hydrogen and oxygen. This is a type of:
Electrolysis is the decomposition of a compound using electrical energy.
Q41. The correct expression for decomposition of silver chloride to silver and chlorine is:
The balanced equation is: 2AgCl(s) → 2Ag(s) + Cl₂(g). Silver chloride decomposes in presence of light.
📚 Case Study 11: Oxidation-Reduction (Redox) Reactions
Oxidation-Reduction reactions involve the transfer of electrons between chemical species. Oxidation is the gain of oxygen or loss of electrons, while reduction is the loss of oxygen or gain of electrons. The oxidizing agent gets reduced while the reducing agent gets oxidized.
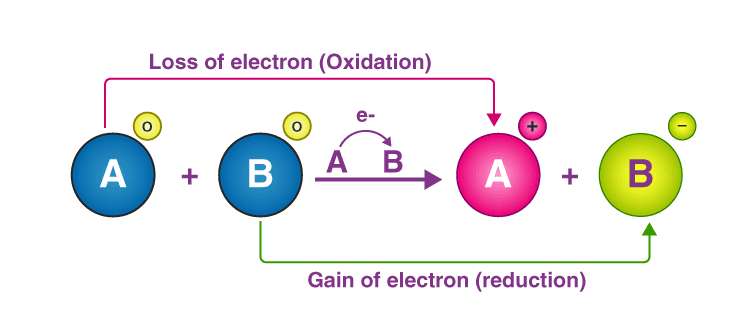
Answer the following questions:
Q42. The gain of oxygen is known as:
Oxidation is defined as gain of oxygen or loss of electrons.
Q43. The oxidation number for oxygen will always be:
Oxygen typically has an oxidation number of -2 in most compounds (except in peroxides where it’s -1).
Q44. The reduction is the decrease in:
Reduction involves decrease in oxidation number as electrons are gained.
Q45. The reaction in which oxidation and reduction takes place at the same time is called:
Redox reaction is where both oxidation and reduction occur simultaneously.
📚 Case Study 12: Chemical Reactions in Daily Life
We often see substances mixing to form new substances in our daily life. Like making tea involves mixing sugar, tea, milk and water. When heated, it turns into tea. Similarly, adding curd to lukewarm milk and keeping it aside for few hours turns the whole milk into curd. These are examples of chemical reactions.

Answer the following questions:
Q46. The red metal on exposure to air turns black. Identify the metal:
Copper (Cu) is red metal that turns black on exposure to air due to formation of copper oxide (CuO).
Q47. When green coloured ferrous sulphate crystals are heated, the colour changes because:
Initially, FeSO₄·7H₂O loses water of crystallisation and turns white, then decomposes to form brown Fe₂O₃.
Q48. Dilute ferrous sulphate is added to acidified KMnO₄. The purple colour fades because:
KMnO₄ is a strong oxidizing agent that oxidizes Fe²⁺ to Fe³⁺ and itself gets reduced, losing its purple color.
Q49. Pb + CuCl₂ → PbCl₂ + Cu. The above reaction is an example of:
This is a displacement reaction where lead (more reactive) displaces copper from copper chloride.
Q50. The colour of layer that deposits on silver ornaments when exposed to air is:
Silver forms black silver sulphide (Ag₂S) layer when exposed to air containing hydrogen sulphide.
Q51. Corrosion can be prevented by:
All methods – alloying, tinning (coating with tin), and galvanizing (coating with zinc) prevent corrosion.

